Disbursement or Reimbursement
Reimbursements
- Reimbursements refer to out-of-pocket expenses incurred by the payee during the course of rendering services or selling goods to the payer (i.e., Buyer). These expenses are subsequently reimbursed by the payer. Examples of such expenses include airfare, travel, accommodation, telephone charges, and photocopying costs.
Scenario: Imagine Supplier 1 providing services to the customer through a claimant (Supplier 2). Supplier 2 incurs certain expenses (e.g., travel costs, photocopying charges) while rendering services. These expenses are then recovered from the customer as reimbursement.
Disbursements
- Disbursements, on the other hand, are out-of-pocket expenses incurred by the payer (i.e., buyer) and paid directly to a third party by the payee. These expenses are related to services rendered or the sale of goods by the payee to the payer.
Scenario: Suppose a buyer engages Supplier 1 for legal services. Supplier 1 pays a court filing fee (a disbursement) on behalf of the buyer. The buyer reimburses Supplier 1 for this expense.

Key Considerations
Terminology Clarification
- Claimant: A registered person who recovers expenses incurred on behalf of the customer.
- Customer: Any person receiving a service directly or indirectly through a claimant.
- Service Provider: A person providing services to the customer through a claimant.
Methodology for Determining Expenditure
- To classify an expense as either a disbursement or reimbursement for service tax purposes, consider the following:
- Reimbursement: Recovery of an expense from the customer that the claimant (Supplier 2) incurred as a principal from another party.
- Cost: The value of taxable service (exclusive of service tax, if any) incurred by the claimant.
- Primary Service: The main service provided by the claimant as a principal to the customer.

Examples 1
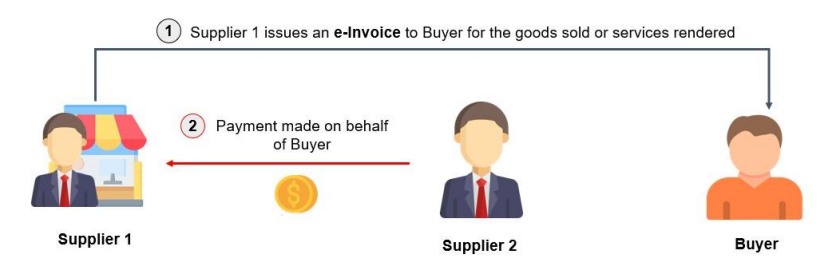
- Supplier 1 issues e-invoices directly to Buyer for goods sold or services provided to Buyer.
- Supplier 2 then makes payment to Supplier 1 in settlement of the aforementioned electronic invoice issued to Buyer in accordance with the arrangements agreed between Supplier 2 and Buyer.
- Therefore, Supplier 2 will issue an e-invoice to the Buyer for the goods sold or services provided by Supplier 2.
- Since Supplier 1 has issued an e-invoice to Buyer, it should not be included in Supplier 2’s e-invoice to Buyer.

The steps involved for the issuance of e-Invoice for the Example 1 above are as follows:
Step 1 ******
- Supplier 2 enters into an agreement with the Buyer for the supply of goods or provision of services. As part of the arrangement, Supplier 2 will make payment on behalf of the Buyer to settle any expenses incurred during the contract period.
Step 2
- Upon concluding a sale or transaction, Supplier 1 issues an e-Invoice directly to the Buyer as per the required fields outlined in below of the e-Invoice Guideline. Supplier 1 then submits the e-Invoice to the IRBM for validation.
i)List of General TIN
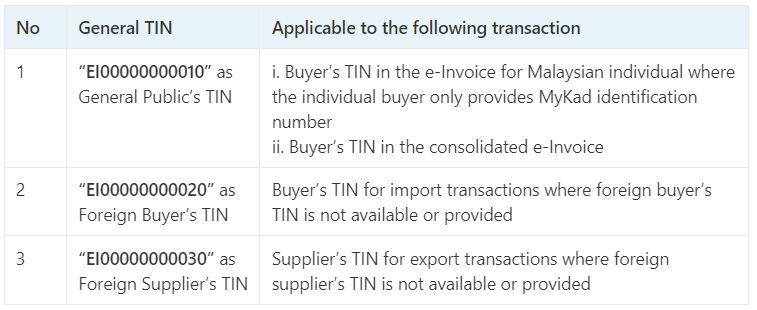
ii)Buyer’s Details in Consolidated E-Invoice

Step 3
- Supplier 2 makes payment on behalf of the Buyer to Supplier 1 to settle the outstanding amount. Supplier 1 issues payment proof to Supplier 2 for the settlement.
Step 4
- Supplier 2 issues an e-Invoice to the Buyer for the goods supplied or services rendered by Supplier 2 to the Buyer. The process of issuing an e-Invoice is similar to Step 2 above. Supplier 2 should neither include the payment made on behalf of the Buyer in Supplier 2’s e-Invoice nor issue an additional e-Invoice for it. Supplier 2 provides payment proof to the Buyer to recover the payment made to Supplier 1 on behalf of the Buyer.
- A Further Details Scenario for Example 1. Perniagaan Adibah hired an event planner to launch their latest product on October 9, 2024. On October 1, 2024, the event planner sourced flowers from a florist for decoration. The florist issued an e-Invoice directly to Perniagaan Adibah for the flowers supplied on October 7, 2024. As per the service contract, the event planner will make payment on behalf of Perniagaan Adibah to settle any outstanding amount incurred and recover the same from Perniagaan Adibah at a later date. On October 8, 2024, the event planner paid RM4,000 to the florist on behalf of Perniagaan Adibah for the flowers purchased. On October 12, 2024, the event planner issued an e-Invoice to Perniagaan Adibah for services rendered. The event planner should only include the service fee in the e-Invoice to Perniagaan Adibah, along with the other charges. However, the RM4,000 paid on behalf should not be included in the event planner’s e-Invoice. For the purpose of recovering the RM4,000 paid on behalf of Perniagaan Adibah to the florist, the event planner provides a copy of the payment proof to Perniagaan Adibah.
Example 2

- When Supplier 1 issues an e-Invoice to Supplier 2 for goods sold or services rendered to the Buyer, Supplier 2 will make payment to Supplier 1 based on the agreed arrangement between Supplier 2 and the Buyer.
- In turn, Supplier 2 will issue a separate e-Invoice to the Buyer, recording the amount incurred on behalf of the Buyer in addition to the goods sold or services rendered by Supplier 2.
- The e-Invoice will present these as separate line items, with one line for service fee charges and another line for disbursement/reimbursement.

The steps involved for issuance of e-Invoice for Example 2 above are as follows:
Step 1
- Supplier 2 enters into an agreement with the Buyer for the supply of goods or provision of services. As part of the arrangement, Supplier 2 will make payment on behalf of the Buyer to settle any expenses incurred during the contract period.
Step 2
- Upon concluding a sale or transaction, Supplier 1 issues an e-Invoice to Supplier 2 as per the required fields outlined the e-Invoice Guideline. Supplier 1 then submits the e-Invoice to the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) for validation.
Step 3
- Supplier 2 makes payment to Supplier 1. Supplier 1 issues payment proof to Supplier 2 for the settlement.
Step 4
- Supplier 2 issues an e-Invoice to the Buyer (similar to Step 2 above) to record the amount incurred on behalf of the Buyer (e.g., disbursement/reimbursement) alongside the goods sold or service rendered by Supplier 2, which will be presented as separate line items in the e-Invoice.
- A Further Details Scenario for Example 2. Same facts as in further details scenario for example 1, except that now the event planner has incurred RM30,000 to rent a hotel banquet hall for the product launch event. An e-Invoice has been issued by the hotel to the event planner. The event planner will issue an e-Invoice to charge Perniagaan Adibah for the services provided and to recover the rental cost of the hotel banquet hall. The e-Invoice issued by the event planner will present separate line items for the service fee and the rental of the hotel banquet hall.
Conclusion
Understanding the fine distinctions between disbursement and reimbursement is essential for tax compliance and efficient financial management. As Malaysia embraces e-invoicing, staying informed about these concepts ensures smooth business operations and fosters trust between stakeholders.
Remember, while we strive for precision, always consult professional advice and refer to official guidelines for specific cases.

Disclaimer: The information provided on this platform is for general informational purposes only. It does not constitute professional advice and should not be relied upon for making decisions. Wanconnect Consulting Group is not responsible for any errors or omissions in the content or for any actions taken based on the information provided. We recommend seeking professional advice for specific situations. Wanconnect Consulting Group reserves the right to modify, update, or remove any content without notice.
Wanner to ask the reimbursement means is payment on behalf that the invoice is under customer’s name.
Disbursement means payment on behalf that the invoice is under our co’s name.
Is it I’m right . Tq
For more info, please visit our FB page.